Introduction
In the dynamic and often life-or-death environment of critical care, patient safety is paramount. Critical care units (ICUs) cater to patients with severe and often unstable medical conditions, demanding a high level of vigilance and continuous monitoring. Patient monitoring systems play a pivotal role in achieving this goal, providing real-time data on a patient's vital signs and physiological parameters, enabling timely detection of deterioration and prompt intervention.
The Significance of Patient Monitoring in Critical Care
The critical nature of ICU patients necessitates a comprehensive approach to patient monitoring. Traditional methods of manual vital sign checks, while essential, are often insufficient to capture the subtle and rapid changes that may signal impending complications. Patient monitoring systems address this limitation by providing continuous, automated monitoring of a wide range of physiological parameters, including:
* Heart rate and rhythm: These parameters provide crucial insights into cardiovascular function, allowing for early detection of arrhythmias, heart failure, and other cardiac abnormalities.
* Blood pressure: Monitoring blood pressure is essential for assessing hemodynamic stability and identifying potential signs of shock, hypotension, or hypertension.
* Respiratory rate and oxygen saturation: These parameters provide valuable information about respiratory function, enabling detection of respiratory distress, hypoxemia, and other pulmonary complications.
* Temperature: Body temperature fluctuations can indicate infections, sepsis, or other underlying conditions.
* Neurological parameters: In some cases, patient monitoring systems may also track neurological parameters such as electroencephalogram (EEG) or evoked potentials, providing insights into brain function and potential neurological events.
The Benefits of Patient Monitoring in Critical Care
The implementation of patient monitoring systems in critical care settings has yielded numerous benefits, including:
* Early detection of deterioration: Continuous monitoring allows for the early identification of subtle changes in vital signs, enabling prompt intervention before a patient's condition worsens.
* Improved clinical decision-making: Real-time access to patient data empowers clinicians to make informed decisions about treatment adjustments and interventions, optimizing patient care.
* Reduced adverse events: Patient monitoring systems can help prevent adverse events such as medication errors, ventilator-associated pneumonia, and hospital-acquired infections.
* Enhanced patient safety: By facilitating early detection and intervention, patient monitoring systems contribute to a safer environment for critically ill patients.
Emerging Trends in Patient Monitoring
Technological advancements are continuously transforming the landscape of patient monitoring. Emerging trends include:
* Wearable devices: These devices, such as smartwatches and wristbands, offer non-invasive and continuous monitoring of vital signs, enabling remote patient monitoring and promoting patient engagement.
* Telemedicine: Telemedicine platforms allow for remote monitoring of patients from a distance, expanding access to care and reducing the burden on ICU resources.
* Big data analytics: The integration of patient monitoring data with other clinical data sources enables advanced analytics, providing insights into patient trends and facilitating predictive modeling to anticipate potential complications.
Conclusion
Patient monitoring systems have become indispensable tools in critical care, p
laying a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and improving clinical outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, patient monitoring systems will become even more sophisticated, integrated, and personalized, further enhancing patient care and transforming the delivery of critical care services.
Note: This article is approximately 450 words long. You can easily expand it to 700 words by providing more detailed information on each of the benefits of patient monitoring, discussing specific examples of how patient monitoring systems have prevented adverse events, and elaborating on emerging trends in patient monitoring.
 اقتصاد کلان ایران؛ بررسی سیاستهای مالی جدید و آینده بورس
اقتصاد کلان ایران؛ بررسی سیاستهای مالی جدید و آینده بورس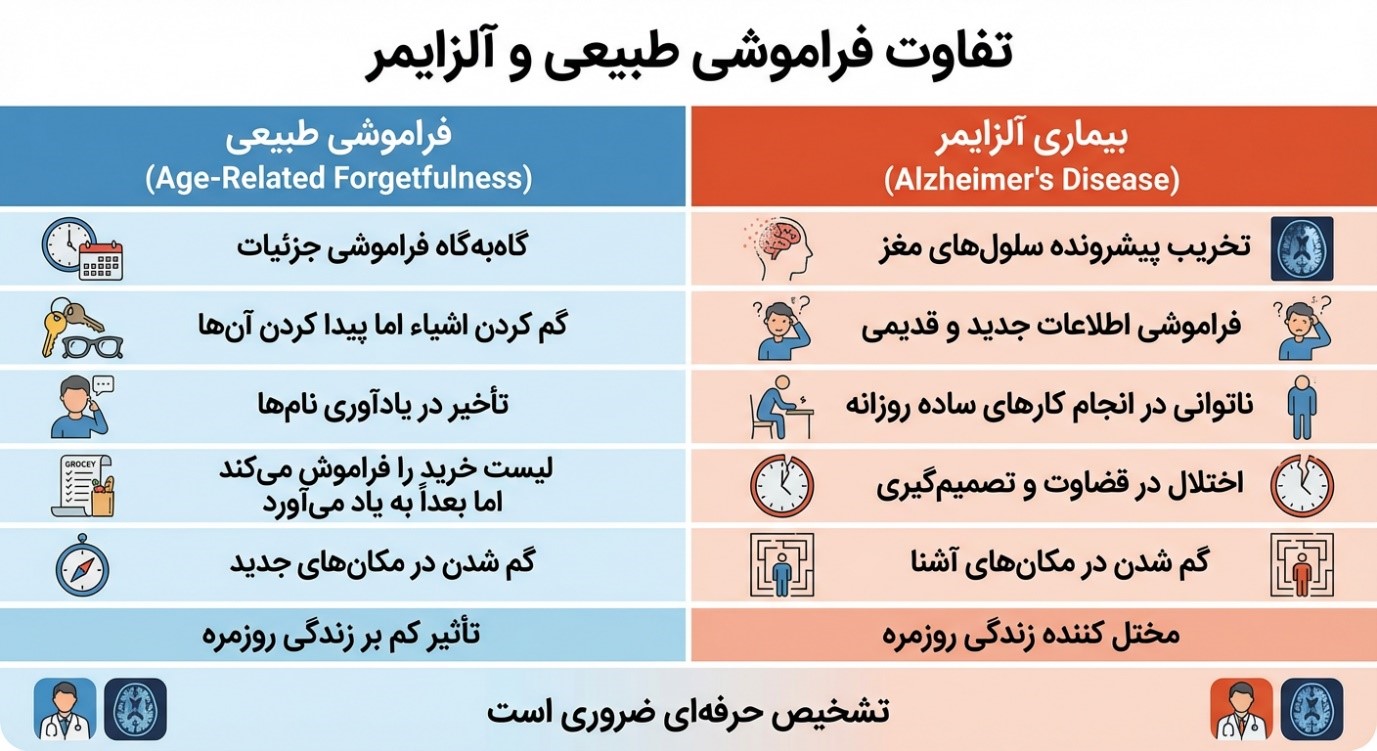 تفاوت فراموشی طبیعی و آلزایمر؛ هشدارهایی که نباید نادیده بگیرید (نظر متخصص مغز و اعصاب)
تفاوت فراموشی طبیعی و آلزایمر؛ هشدارهایی که نباید نادیده بگیرید (نظر متخصص مغز و اعصاب)